Gut health is a topic that has garnered significant attention in recent years, and for good reason. The gut, often referred to as the “second brain,” plays a crucial role in our overall health and well-being. It is home to trillions of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi, collectively known as the gut microbiota. These microorganisms are essential for various bodily functions, including digestion, immune response, and even mental health. Understanding the importance of gut health and how to maintain it can have profound effects on your overall well-being.
The Gut Microbiota: A Delicate Balance
The gut microbiota is a complex and dynamic community of microorganisms that inhabit the digestive tract. It consists of beneficial bacteria that aid in digestion, nutrient absorption, and protection against harmful pathogens. A healthy gut microbiota is characterized by a diverse and balanced microbial community. Disruptions to this balance, known as dysbiosis, can lead to various health issues, including inflammatory bowel disease, obesity, diabetes, and mental health disorders.
The Gut-Brain Axis: A Two-Way Communication
The gut and the brain are connected through a bidirectional communication network known as the gut-brain axis. This connection is facilitated by the vagus nerve, hormones, and neurotransmitters produced by gut bacteria. The gut-brain axis plays a pivotal role in regulating mood, stress response, and cognitive function. For instance, the production of serotonin, a neurotransmitter that regulates mood, is significantly influenced by gut bacteria. This explains why gut health is closely linked to mental health conditions such as anxiety and depression.
The Immune System and Gut Health
Approximately 70% of the immune system resides in the gut. The gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT) is responsible for producing immune cells and antibodies that protect against infections and maintain immune tolerance. A healthy gut microbiota supports the development and function of the immune system by promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria and inhibiting the growth of harmful pathogens. Dysbiosis, on the other hand, can compromise the immune system and increase susceptibility to infections and autoimmune diseases.
Diet and Gut Health
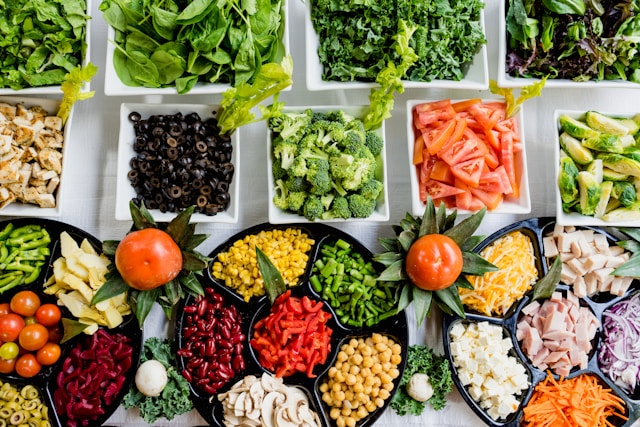

Diet plays a critical role in shaping the gut microbiota. A diet rich in fiber, prebiotics, and probiotics can promote a healthy and diverse gut microbiota. Here are some dietary tips to support gut health:
- Fiber-Rich Foods: Fiber acts as a prebiotic, feeding the beneficial bacteria in the gut. Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes in your diet.
- Fermented Foods: Fermented foods such as yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi contain probiotics, which are live beneficial bacteria that can enhance gut health.
- Limit Processed Foods and Sugars: Processed foods and sugars can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria and promote the growth of harmful pathogens. Opt for whole, unprocessed foods whenever possible.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps maintain the mucosal lining of the intestines and supports the balance of gut bacteria.
- Avoid Excessive Antibiotic Use: While antibiotics are necessary for treating bacterial infections, overuse can disrupt the gut microbiota. Use antibiotics only when prescribed by a healthcare professional.
Lifestyle Factors and Gut Health
In addition to diet, several lifestyle factors can influence gut health:
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity has been shown to promote the growth of beneficial gut bacteria and improve overall gut health.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can negatively impact the gut microbiota and contribute to digestive issues. Practice stress management techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, and yoga.
- Adequate Sleep: Poor sleep quality and sleep deprivation can disrupt the gut microbiota and lead to gastrointestinal problems. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night.
- Avoid Smoking and Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Both smoking and excessive alcohol intake can harm the gut microbiota and increase the risk of gastrointestinal diseases.
Final Words
Understanding and maintaining gut health is essential for overall well-being. A healthy gut microbiota supports digestion, immune function, and mental health. By adopting a balanced diet rich in fiber and probiotics, managing stress, exercising regularly, and avoiding harmful substances, you can promote a healthy gut and enhance your overall health. Prioritize your gut health, and you’ll reap the benefits of improved digestion, a stronger immune system, and better mental well-being.




