Pain is a complex and multifaceted experience that affects millions of people worldwide. While conventional medicine often relies on pharmaceuticals to manage pain, holistic approaches offer alternative methods that address the mind, body, and spirit. These approaches can be particularly beneficial for chronic pain management, providing relief without the side effects associated with many medications. This comprehensive guide explores various holistic methods to manage pain and improve overall well-being.
Understanding Holistic Pain Management
Holistic pain management involves treating the whole person rather than just the symptoms of pain. It encompasses physical, emotional, and spiritual dimensions, aiming to promote overall health and balance. This approach recognizes that pain is not solely a physical experience but also influenced by emotional and psychological factors.
1. Mind-Body Techniques
Mind-body techniques are practices that harness the connection between mental and physical processes to manage pain. These techniques can help reduce stress, enhance relaxation, and improve coping skills.
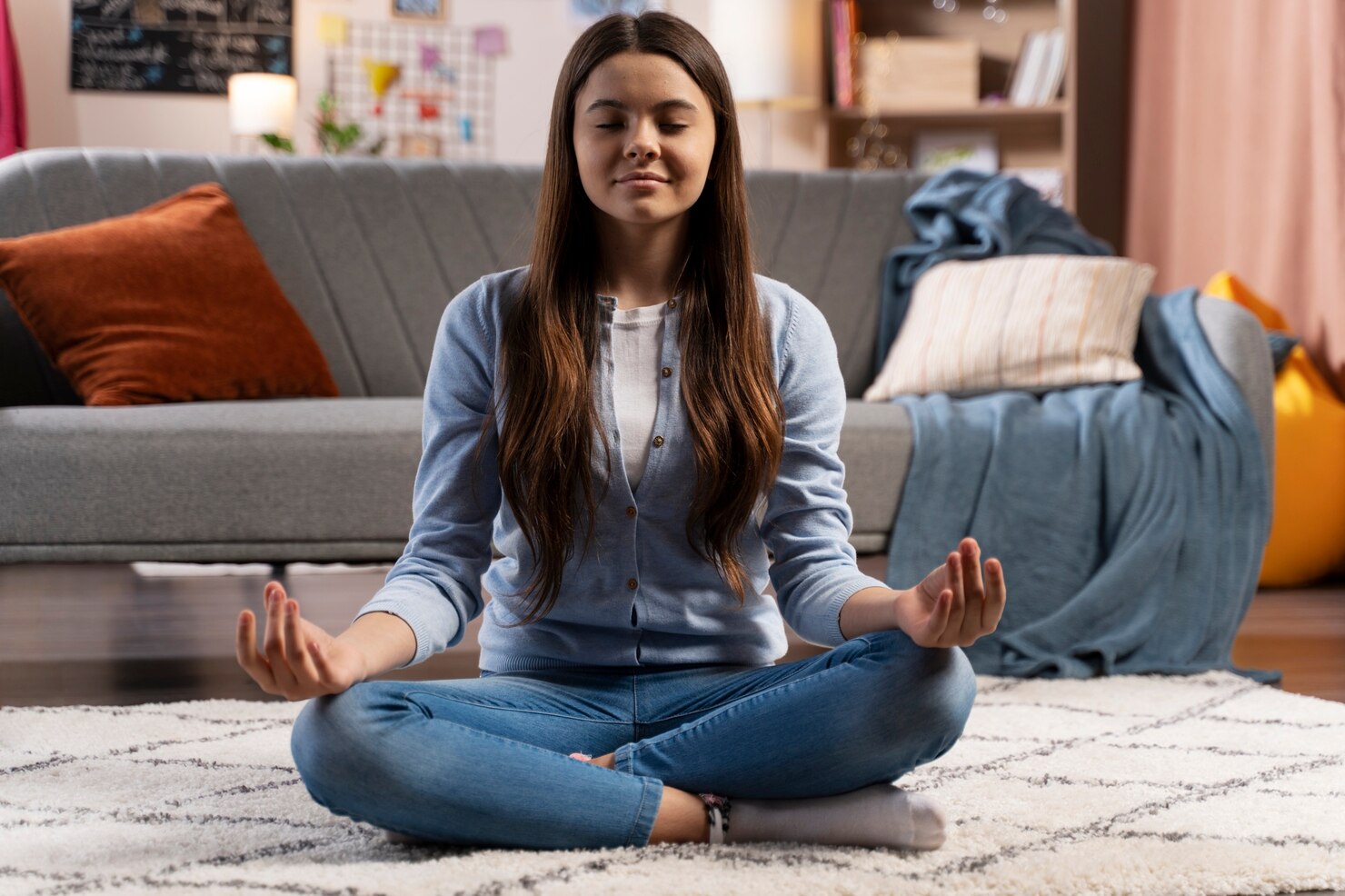

Meditation and Mindfulness
Meditation and mindfulness practices can significantly reduce the perception of pain and improve quality of life. Mindfulness involves focusing on the present moment without judgment, which can help patients become more aware of their pain and manage it more effectively.
- Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR): This program combines mindfulness meditation and yoga to help individuals manage pain and stress. Research has shown that MBSR can reduce chronic pain and improve physical and emotional well-being.
- Guided Imagery: This technique involves visualizing positive images to promote relaxation and reduce pain. It can be particularly effective for conditions like fibromyalgia and arthritis.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT is a type of psychotherapy that helps individuals change negative thought patterns and behaviors related to pain. It teaches coping strategies and problem-solving skills to manage pain more effectively. Studies have shown that CBT can reduce pain intensity, improve mood, and enhance overall quality of life.
2. Physical Therapies
Physical therapies focus on improving physical function and reducing pain through movement and manipulation.
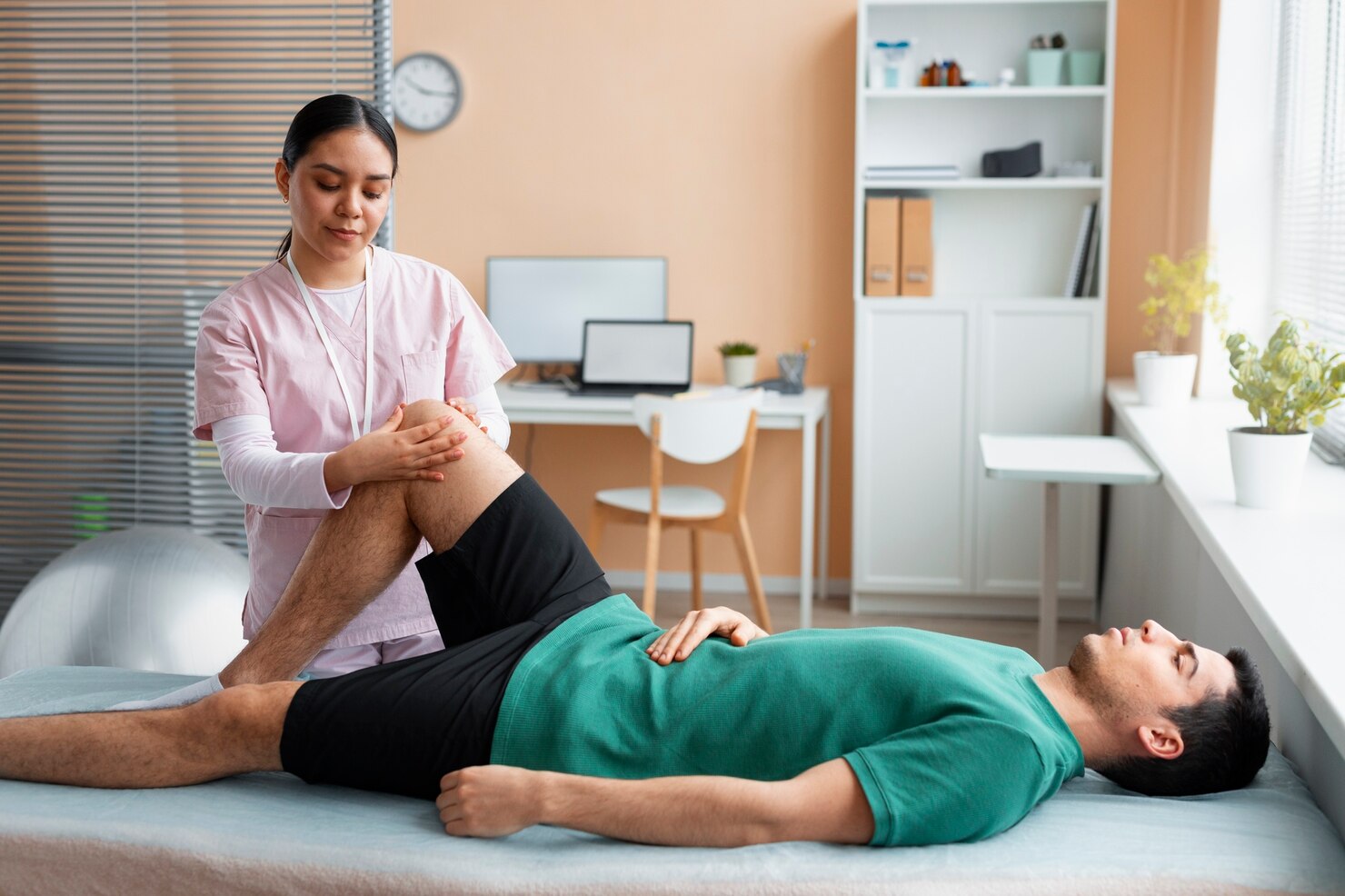

Exercise
Regular physical activity is one of the most effective ways to manage chronic pain. Exercise releases endorphins, which are natural pain relievers. It also improves flexibility, strength, and overall physical health.
- Low-Impact Activities: Activities such as walking, swimming, and cycling can be beneficial for people with chronic pain. These exercises are gentle on the joints and help maintain mobility.
- Strength Training: Building muscle strength can reduce the strain on painful joints and improve posture, leading to less pain over time.
Yoga and Tai Chi
Both yoga and tai chi combine physical movement with mindfulness and breath control. These practices can enhance flexibility, strength, and balance while promoting relaxation and stress reduction.
- Yoga: Research has shown that yoga can reduce chronic pain and improve physical function in conditions such as lower back pain and arthritis.
- Tai Chi: This ancient Chinese practice involves slow, deliberate movements and deep breathing. Studies have demonstrated its effectiveness in reducing pain and improving quality of life for people with chronic pain conditions.
Acupuncture
Acupuncture is a traditional Chinese medicine practice that involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body. It is believed to balance the body’s energy flow and has been shown to provide relief for various pain conditions, including migraines, osteoarthritis, and lower back pain.
Chiropractic Care
Chiropractic care involves the manipulation of the spine and other parts of the body to alleviate pain and improve function. It is particularly effective for musculoskeletal pain, such as back pain and headaches.
3. Nutritional Approaches
Diet and nutrition play a crucial role in pain management. Certain foods have anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce pain, while others may exacerbate it.

Anti-Inflammatory Diet
An anti-inflammatory diet focuses on consuming foods that reduce inflammation in the body. Key components include:
- Fruits and Vegetables: Rich in antioxidants and phytochemicals, these foods help combat inflammation. Berries, leafy greens, and cruciferous vegetables are particularly beneficial.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Found in fatty fish (such as salmon and mackerel), flaxseeds, and walnuts, omega-3s have powerful anti-inflammatory effects.
- Whole Grains: Foods like oats, brown rice, and quinoa provide fiber and nutrients that can reduce inflammation.
- Healthy Fats: Olive oil, avocado, and nuts are sources of healthy fats that can help reduce inflammation.
Avoiding Pro-Inflammatory Foods
Certain foods can increase inflammation and worsen pain. These include:
- Processed Foods: High in unhealthy fats, sugars, and additives, processed foods can contribute to inflammation.
- Refined Sugars and Carbohydrates: These can spike blood sugar levels and promote inflammation.
- Red and Processed Meats: These foods contain high levels of saturated fats and can increase inflammation.
4. Herbal and Natural Supplements
Several herbs and natural supplements have been shown to reduce pain and inflammation.

Turmeric
Turmeric contains curcumin, a compound with potent anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. It can help reduce pain associated with arthritis and other inflammatory conditions.
Ginger
Ginger has anti-inflammatory effects similar to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). It can be effective in reducing pain and inflammation in conditions like osteoarthritis.
Boswellia
Also known as Indian frankincense, boswellia has been used for centuries to treat inflammation and pain. It can be particularly helpful for rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease.
Capsaicin
Derived from chili peppers, capsaicin is commonly used in topical creams and patches to relieve pain. It works by depleting substance P, a compound that transmits pain signals to the brain.
5. Lifestyle Changes

Making certain lifestyle changes can significantly impact pain management and overall health.
Stress Management
Chronic stress can exacerbate pain. Techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, and mindfulness can help manage stress levels and reduce pain.
Sleep Hygiene
Poor sleep can worsen pain perception. Establishing good sleep hygiene practices, such as maintaining a regular sleep schedule and creating a restful environment, can improve sleep quality and reduce pain.
Hydration
Staying hydrated is essential for overall health and can help reduce pain. Dehydration can exacerbate muscle pain and joint stiffness.
Combining Holistic Approaches
A comprehensive pain management plan often involves combining multiple holistic approaches. For instance, incorporating regular exercise, a balanced diet, stress management techniques, and physical therapies can provide synergistic benefits. It’s essential to find a combination of methods that work best for you and to consult with healthcare professionals to ensure a safe and effective pain management strategy.